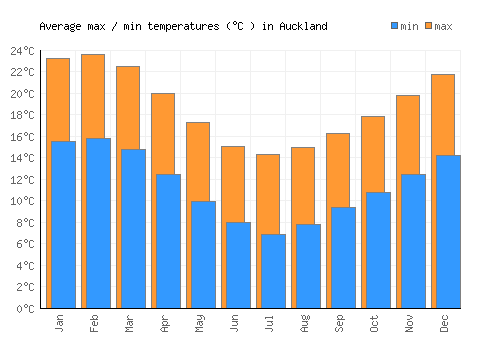
Auckland, known as the “City of Sails,” boasts a unique climate influenced by its coastal location, diverse geography, and proximity to the Southern Hemisphere. Understanding the yearly temperature fluctuations in Auckland is crucial for residents, businesses, policymakers, and researchers alike. This article delves into the intricacies of Auckland’s climate, exploring the factors shaping its temperature patterns and the significance of monitoring these changes. You can also read this The Importance of Brand Visibility: How It Drives Success
Exploring Auckland’s Climate Dynamics
Situated in the North Island of New Zealand, Auckland experiences a temperate maritime climate characterized by mild, damp winters and warm, humid summers. The region’s climate is primarily influenced by two main factors: its proximity to the ocean and its location within the Southern Hemisphere.
The Influence of Ocean Currents and Geography
Auckland’s position on the coast of the Tasman Sea and the Pacific Ocean plays a significant role in shaping its climate. The surrounding water bodies act as heat sinks, moderating temperature extremes throughout the year. Additionally, Auckland’s diverse geography, including harbors, hills, and plains, contributes to microclimatic variations across the region.
Understanding Yearly Temperature Variability
Yearly temperature variations in Auckland reflect broader climate trends influenced by natural phenomena such as El Niño and La Niña, as well as anthropogenic factors like urbanization and climate change. Tracking these fluctuations provides valuable insights into long-term climate patterns and helps inform adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Climate Change and Auckland’s Future
As global temperatures rise due to human activities, Auckland faces potential impacts such as more frequent and intense heat waves, changes in rainfall patterns, and sea-level rise. Understanding how these trends intersect with Auckland’s yearly temperature variations is essential for developing resilient infrastructure, safeguarding ecosystems, and protecting public health.
The Role of Data and Monitoring
Accurate and reliable data collection is fundamental to understanding Auckland’s yearly temperature trends. Meteorological stations across the region collect temperature readings at regular intervals, providing invaluable information for climate scientists, policymakers, and the public. Advances in technology, including satellite remote sensing and climate modeling, enhance our ability to monitor and analyze temperature data with greater precision.
Implications for Urban Planning and Infrastructure
Auckland’s yearly temperature variations have implications for urban planning and infrastructure development. Strategies such as green infrastructure, urban heat island mitigation, and sustainable design can help manage temperature extremes, enhance urban resilience, and improve the overall quality of life for residents.
Adapting to a Changing Climate
Adapting to Auckland’s changing climate requires collaborative efforts from government, businesses, communities, and individuals. Implementing climate-resilient policies, investing in sustainable practices, and raising awareness about climate impacts are crucial steps towards building a more resilient and sustainable future for Auckland.
Conclusion
Auckland’s yearly temperature fluctuations offer valuable insights into the region’s climate dynamics and broader climate trends. By understanding the factors driving these variations and their implications for the future, stakeholders can make informed decisions to mitigate risks, enhance resilience, and ensure a sustainable environment for future generations. Monitoring Auckland’s yearly temperature is not just about tracking numbers; it’s about safeguarding our city’s future in the face of a changing climate.